Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Editorial Board
International Editorial Board
List of Reviewers
Abstracting and indexing
Ethical standards and procedures
REMV in Social Media
Contact
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Authors
Manuscript formatting template
Title page
Highlights
Payments
‘Ghostwriting’ and ‘Guestauthorship’
Guidelines for Referees
The relationship between service quality and occupants’ satisfaction: A mixed-use building
1
Centre for Research in Development, Social & Environment, Faculty Social Sciences & Humanities, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
2
Department of Building and Property Management, Faculty of Accountancy and Management, University Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia
3
Faculty of Architecture, Planning and Surveying, Universiti Teknologi MARA, 40400 Shah Alam, Malaysia
Submission date: 2022-08-24
Final revision date: 2022-10-11
Acceptance date: 2022-11-02
Publication date: 2023-03-10
Corresponding author
Fatin Umaira Muhamad Azian
Centre for Research in Development, Social & Environment, Faculty Social Sciences & Humanities, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
Centre for Research in Development, Social & Environment, Faculty Social Sciences & Humanities, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
REMV; 2023;31(1):78-87
HIGHLIGHTS
- mixed-use buildings
- service quality
- property management
- occupant satisfaction
KEYWORDS
service qualitymixed-use buildingsproperty managementoccupant satisfactionPartial Least Squares Structural Equation Model (PLS-SEM) Analysis
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
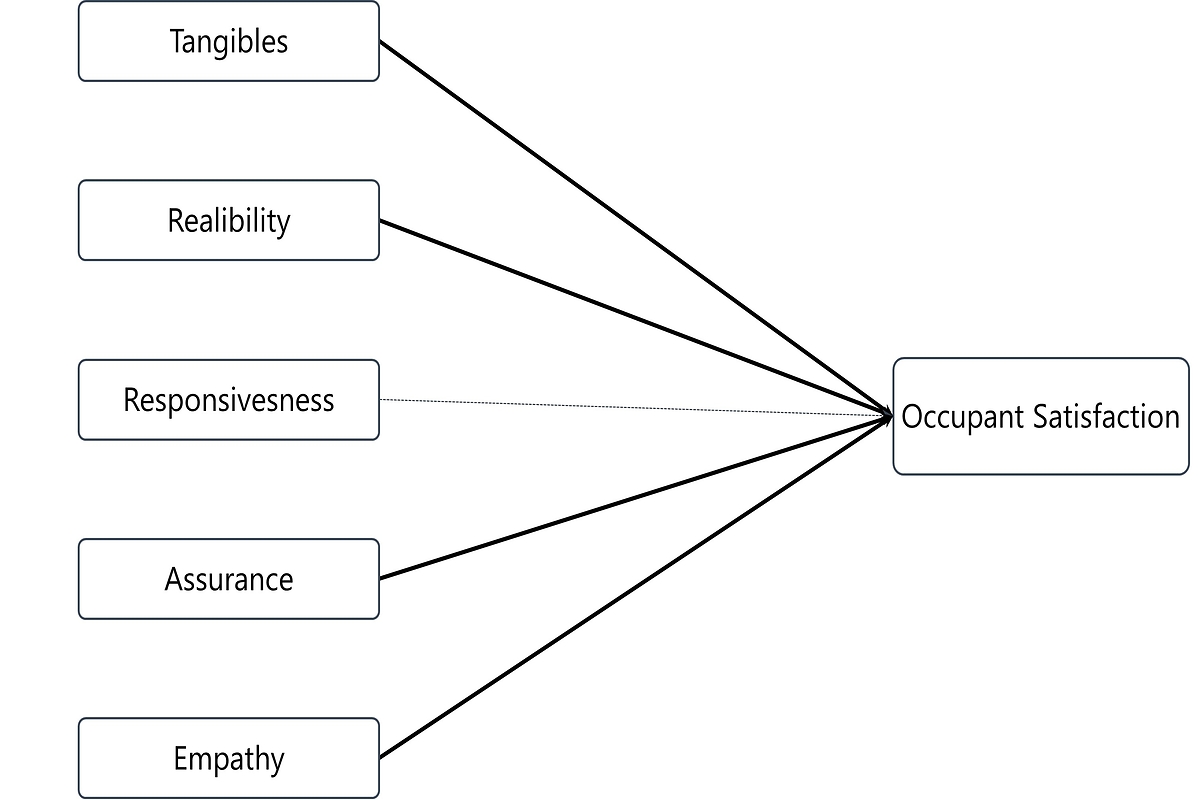
In order to accommodate the city's growing population and land shortage, more vertical buildings are being built nowadays, and mixed-use buildings, as opposed to those with a specific purpose, like residences and businesses, are being developed. Due to the structure's complexity, this building nonetheless presents several issues to property management. Property management companies must comprehend people's current needs and wishes to keep up with satisfaction levels and service quality. As a result, this study aims to ascertain how well a building's services are provided in relation to how satisfied its residents are. A total of 500 respondents were surveyed, and a partial least squares structural equation model (PLS-SEM) analysis was performed to determine the relationships between the variables. The empirical results of this study revealed that four out of the five independent variables, i.e. tangibles, reliability, assurance, and empathy, show a significant relationship with occupants' satisfaction. These research findings may give current insight for property management firms and personnel to improve the quality of their services by implementing corrective measures and prioritizing work, which increases resident satisfaction.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Centre for Research in Development, Social & Environment, Faculty of Social Sciences & Humanities, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman dan Universiti Teknologi MARA for encouraging this research.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.