Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Editorial Board
International Editorial Board
List of Reviewers
Abstracting and indexing
Ethical standards and procedures
REMV in Social Media
Contact
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Authors
Manuscript formatting template
Title page
Highlights
Payments
‘Ghostwriting’ and ‘Guestauthorship’
Guidelines for Referees
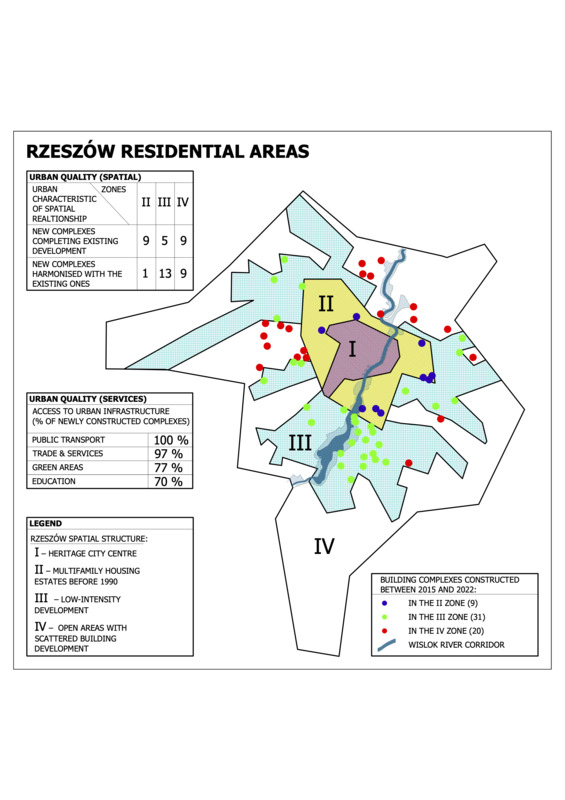
Urban quality in growing cities. The case of Rzeszów, Poland
1
Cracow University of Technology, Poland
2
Rzeszow University of Technology, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-03-30
Final revision date: 2025-01-22
Acceptance date: 2025-02-25
Publication date: 2025-06-24
REMV; 2025;33(2):83-96
HIGHLIGHTS
- quality of urban life means residents' level of well-being within urban environment
- the free market economy started in Poland in 1990 changed investment conditions
- the study reveals how supplementary building development affected the urban quality
KEYWORDS
housing environmenturban quality of lifeindicators of urban qualityurban structuresupplementary building development
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
The economic transformation, which started in 1990 in Poland, opened the possibility to produce and offer flats and apartments in the free market. Since 1990, developers have constructed about 4 million flats, increasing housing resources by more than 30%. The building quality (technologies and materials implemented) improved significantly compared to structures from the pre-transformation period. New investments have been located mainly in cities and city outskirts, complementing the existing development in medium or low development density or open areas, rarely followed by new infrastructure: roads, public transportation, recreational areas and services. These elements define urban quality, an essential indicator of the quality of life. Increasing the density of development threatens the city's urban structure and worsens the urban quality and residents' satisfaction. Such phenomena also hamper achieving sustainable development goals. For this study, one of the most dynamically growing cities, Rzeszow, representing a group of medium-sized cities in Poland, was selected and investigated to assess the urban quality of districts/neighborhoods where new housing complexes appeared after 2010. After identifying and describing the essential elements that provide urban quality in cities in Poland and the factors shaping them, the paper presents the survey results that reveal the quality of the neighborhood system, including residential development constructed after 2010.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.